The combined pill is one of the most popular forms of contraception. This factsheet, by fpa will help decide if it's the right birth-control method for you.
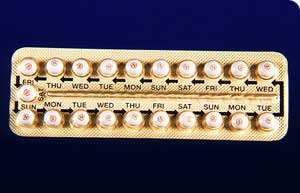
What is it and how does it work?
The combined pill is also known as the Pill. There are many different types, but all contain two hormones: oestrogen and progestogen.
The Pill is more than 99 per cent effective if taken according to instructions. This means that using this method, fewer than one woman in 100 will get pregnant in a year.
The Pill can be started up to and including the fifth day of a period and immediately protects against pregnancy. If started on any other day, an extra method of contraception must also be used for seven days.
The main way the Pill works is by stopping the ovaries releasing an egg each month (ovulation).
It also stops sperm reaching the egg by thickening the mucus from the cervix and stops an egg from settling in the womb. A pill is taken every day for 21 days until the pack is finished. Then you have a seven-day break when you get a bleed. The next pack is started on the eighth day. Every day (ED) pills have 21 active pills and seven placebo tablets. These are taken all the time without a break.
Advantages
• Doesn't interfere with sex.
• Makes periods shorter, lighter and less painful.
• Protects against cancer of the ovary and womb.
• Protects against some pelvic infections.
• Can help with premenstrual tension.
• Reduces the risk of fibroids (non-cancerous tumours in the womb) and ovarian cysts.
Disadvantages
• Temporary side effects include headaches, weight gain, breast tenderness, mood changes, nausea and bleeding between periods.
• May increase blood pressure.
• Rare but serious side effects can include blood clots.
• There is a very small increased risk of breast cancer and cervical cancer.
• Some prescription drugs or complementary medicines may affect how the Pill works.
Can anyone use the combined pill?
TThe Pill doesn't suit everyone but for the vast majority of women the benefits outweigh any risks. Reasons not to use it include if you think you might be pregnant or you are a smoker aged 35 or older.
You also shouldn't use it if you have now or have had in the past:
• blood clots in any vein or artery
• circulatory disease or a heart abnormality
• very severe migraine or migraine with aura
• diabetes with complications
• breast cancer
• active liver or gall bladder disease
What to do if you forget a pill
It's important to take the combined pill at a regular time every day.
You should not take your pill later than 24 hours after your chosen time. If you do, you must treat this as a missed pill day. Do not stop taking your pill and take your next pill at the normal time.
Missing one pill anywhere in your pack or starting your pack one day late is not a problem. Depending on which type of Pill you take, missing more than one pill or starting the packet more than one day late could affect your contraceptive cover. If this happens seek advice.
If you're sick within two hours of taking the pill it will not have been absorbed properly. Take another pill as soon as you feel well enough. If you continue to feel sick, seek advice. If have very severe diarrhoea for more than 24 hours this makes your pill less effective. Seek advice.
General comments
Initially you'll be given three months supply of the Pill. You don't need a cervical smear test or internal examination to use the Pill. Some medicines affect how well the pill works, check with your doctor, nurse or pharmacist.
Where to get it
Contraception is free on the NHS. GPs and family planning clinics can prescribe the pill. Call fpa's helpline on 0845 310 1334 (Monday to Friday, 9am to 6pm) for advice on the Pill or visit www.fpa.org.uk.
No comments:
Post a Comment